| Timeline | From October 2023 to 30 October 2027 |
|---|---|
| Theme | Resource security |
| Countries | Zimbabwe |
| Funded by | NWO |
Water hyacinths: Use them or lose them? Improving human and ecosystem health by bringing the science to the people of Lake Chivero, Zimbabwe (WHYimprove)
Water hyacinth (WHY) is an invasive species in (sub-)tropical inland waterbodies that clogs waterways and intakes and affects aquatic life and human activities, and may facilitate the spread of diseases. On the other hand, WHY can be exploited for biofuel production and other sources of income. A sustainable solution to water hyacinth infestation “uses” WHY instead of only attempting to “lose” them. This project uses scientific studies of data collected on site, in the lab and from satellites, combined with stakeholder experiences to co-create such solutions for Lake Chivero, the main source of drinking water to Harare, capital of Zimbabwe.
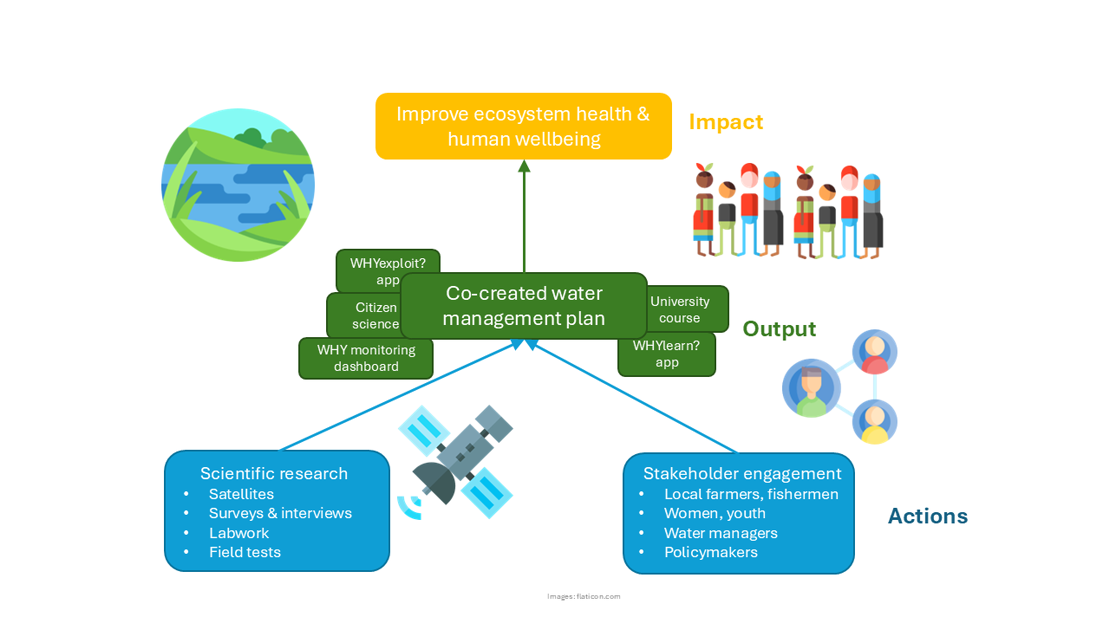
Figure 1: Schematic of the holistic approach of the WHYimprove project (pictograms by flaticon.com)
To be both effective and sustainable, new strategies to manage WHY need to be developed with a holistic view that accounts for humans, society and the ecosystem; users and managers; scientists and stakeholders. Our approach is composed of four elements:
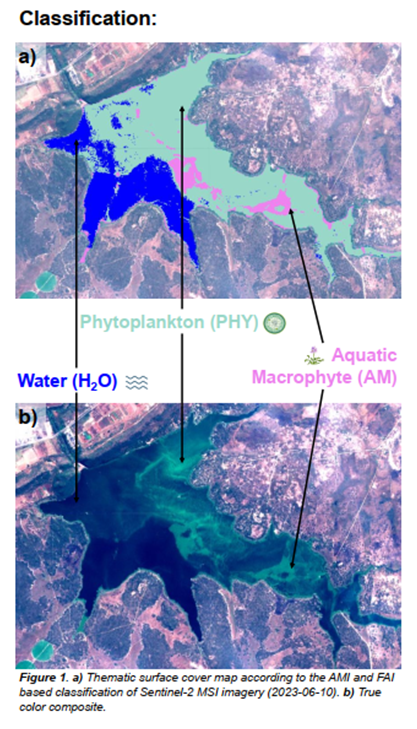
- Fundamental scientific research into causes and effects of WHY and degraded water quality, in which we recognise WHY both as a symptom and as a biomarker of degraded water quality. The research rests on the two pillars of satellite data and local field work
- Collection of stakeholder perspectives – particularly those of local farmers, fishermen, and women, but also, e.g., water managers and healthcare professionals – and integration into the development process of WHY management strategies
- Engaging stakeholders by co-creation efforts from the beginning throughout the project up to, and including its end and evaluation; and by participatory science projects that provide ownership of the WHY management challenge and potential solutions
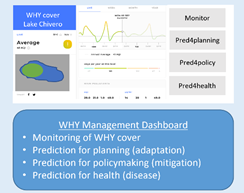
- Knowledge sharing by providing open-access data, tools (mobile phone apps and a dashboard), open-access journal articles, a low-level newsletter, and by educating women on water quality and hygiene
Workpackages
These elements are addressed in six work packages:
Our project will impact the health of the lake ecosystem and the well-being and living conditions for people relying on lakes and reservoirs. This will lead to increased resilience of the ecosystem and its resident communities. Specifically, we aim for three domains of impact:
- More healthy and resilient lake ecosystems;
- improved well-being of people depending on lakes; and
- more resilient lake communities.
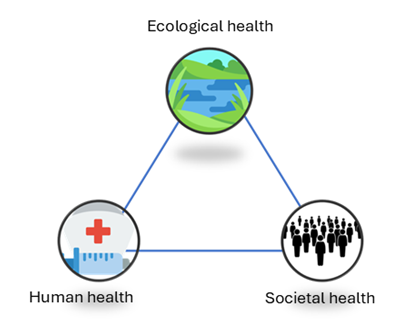
By integrating scientific findings from satellite and empirical data from local communities with stakeholders’ perspectives and recommendations, we will contribute to more resilient lake socio-ecosystems. Linking the health of humans, animals, and their environment (like in the One Health approach) can be useful in mitigating and preventing water-related diseases. The mobile phone applications and the WHY management dashboard are schematically depicted in Fig. 2.4. Together with the WHY management strategies, the MSU undergraduate course, and citizen science projects developed within WP6, they form the main output of the project.